Managing Diabetes with a Keto Lifestyle
When it comes to managing type 2 diabetes, the ketogenic (keto) diet has gained attention for its potential benefits. This blog post will explore how a keto lifestyle can help people with diabetes, the challenges involved, and practical tips for success. Backed by research and real-life experiences, we’ll cover everything you need to know about this low-carb, high-fat approach.
Does the Keto Diet Work for Type 2 Diabetes?
The keto diet has been shown to improve blood sugar control, reduce medication needs, and support weight loss in people with type 2 diabetes. By limiting carbohydrates, it shifts the body’s energy source from glucose to fat, promoting better glycemic control. While it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution, many find success with this lifestyle under proper guidance.
Potential Benefits:
- Better Blood Sugar Control: Lower carbohydrate intake helps stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Reduced Insulin Dependency: Many people reduce or even eliminate their insulin use.
- Weight Loss: Burning fat for energy promotes weight loss, which can improve insulin sensitivity.
- Improved Cholesterol: Higher HDL (“good”) cholesterol and lower triglycerides.
- Sustained Energy Levels: Avoiding sugar crashes means more consistent energy throughout the day.
Challenges:
- Restrictive Nature: The keto diet can feel limiting, especially at social gatherings.
- Keto Flu: Initial symptoms like fatigue, headaches, and irritability.
- Sustainability: Staying consistent with the diet long-term requires planning and commitment.
Research Findings:
- A 2008 study found that keto improved glycemic control and reduced medication needs more than low-glycemic diets.
- A 2017 study showed keto led to better weight loss and A1C improvements over a low-fat diabetes diet.
- Other research supports keto for short-term benefits, but highlights the need for long-term studies.
Monitoring and Safety:
- Test blood sugar and ketones regularly.
- Adjust medications as needed with your doctor’s guidance.
- Stay hydrated and include electrolytes to avoid keto flu.
Risks and Precautions:
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Limited food options can lead to missing vital nutrients.
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): Rare but possible in people with uncontrolled blood sugar.
- Hypoglycemia: Blood sugar may drop too low if medications aren’t adjusted.
- Not Suitable for Everyone: Pregnant women, those with kidney disease, or individuals with eating disorders should avoid keto without medical supervision.
Lessons and Tips for Success:
1. Focus on Whole Foods:
Avoid processed foods and stick to natural options like eggs, avocados, nuts, and leafy greens.
2. Prep Your Meals:
Plan ahead to avoid last-minute temptations and ensure balanced meals.
3. Start Slow:
Ease into keto by gradually reducing carbs and increasing healthy fats.
4. Avoid “Calorie Deficit” Myths:
While keto can naturally reduce calorie intake, focus on high-protein, healthy-fat meals that keep you full and energized.
5. Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water and replenish electrolytes to minimize side effects.
Expert Recommendations:
- Consult Your Doctor: Before starting keto or making any change to your diet, ensure it aligns with your doctor’s recommendations.
- Focus on Whole Foods: Prioritize nutrient-dense, minimally processed options.
- Monitor Progress: Regularly check blood sugar and ketone levels.
- Personalize Your Approach: Customize the diet to fit your lifestyle and preferences.
FAQs
Is the keto diet good for diabetics?
The keto diet helps stabilize blood sugar, improve insulin sensitivity, and support weight loss, making it beneficial for managing type 2 diabetes.
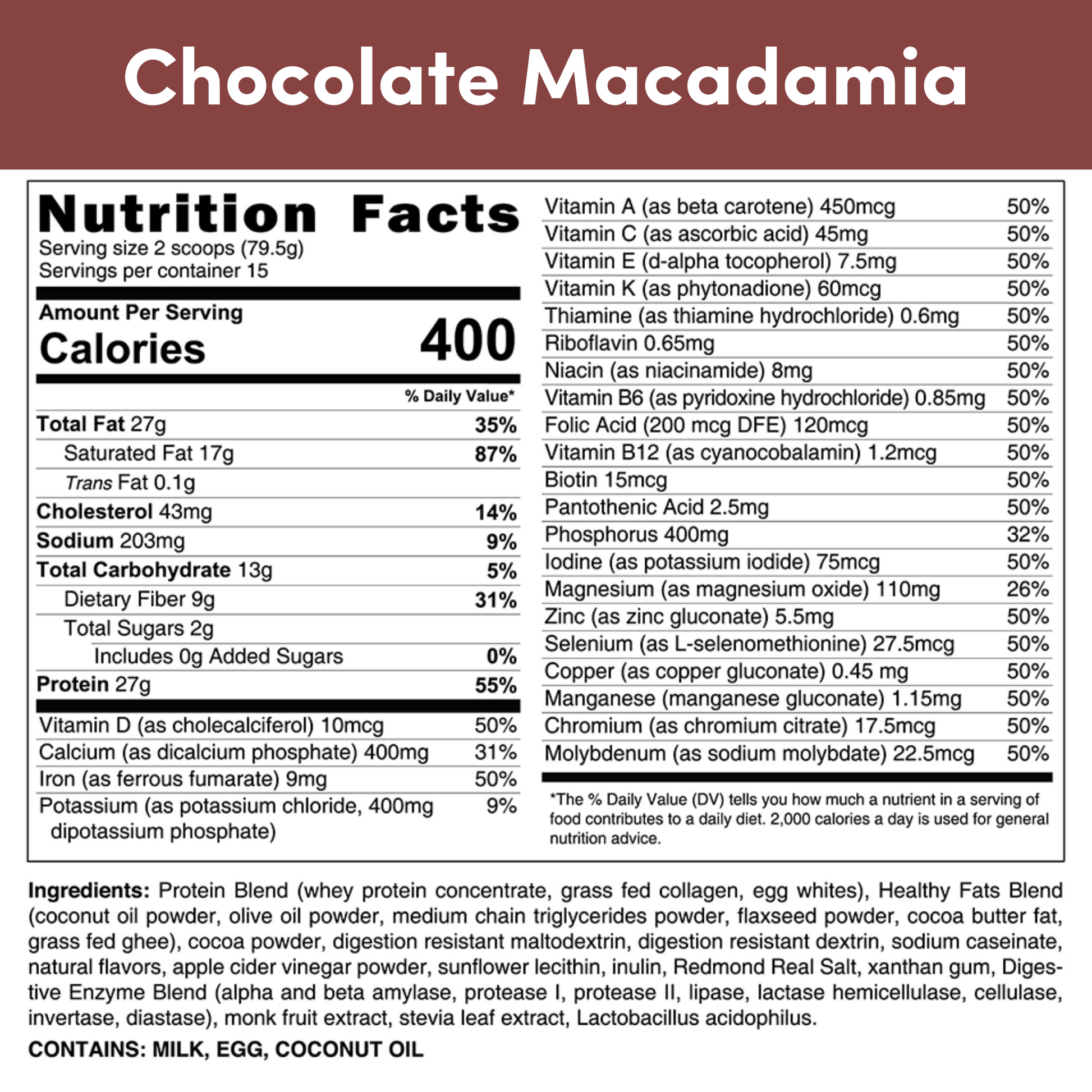
Is Whey Protein for Diabetics?
HLTH Code shakes combine whey protein with egg white and collagen proteins for a balanced, diabetes-friendly meal replacement that supports muscle health and satiety.
Does HLTH Code work for diabetics?
Yes, HLTH Code shakes are meal replacement shakes specifically designed to be low in carbs and high in protein and healthy fats, aligning with keto principles to support diabetes management.
Final Thoughts:
The keto diet offers a promising option for managing type 2 diabetes, but it’s not without its challenges. Consult your doctor, start slowly, and stay consistent. Whether through keto, a balanced diet, or HLTH Code shakes, finding a sustainable approach is key to long-term health.
This article is for informational and educational purposes only. It is not, nor is it intended to be substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment and should never be relied upon for specific medical advice.
















 30 Day Money Back Guarantee
30 Day Money Back Guarantee